
Worksheet - Lewis Dot. For each of the following, draw the Lewis Dot Structure, give the electron arrangement (E.A.) and the molecular geometry (M.G.): PF 5. Demos Lewis Dot Structures. This demo will convert a skeletal figure, provided by a drawing in the HTML5 SketcherCanvas component on the left, into a Lewis Dot Structure in the Canvas on the right. When you are finished drawing your 2D structure, click on the Get Lewis Dot Structure button to see the result.
In 1916, ten years before the Schrodinger wave equation, G. N. Lewis suggested that a chemical bond involved sharing of electrons. He described what he called the cubical atom
, because a cube has 8 corners, to represent the outer valence shell electrons which can be shared to create a bond. This was his octet rule.
Search by Structure or Substructure. Upload a structure file or draw using a molecule editor. A Lewis electron dot diagram (or electron dot diagram or a Lewis diagram or a Lewis structure) is a representation of the valence electrons of an atom that uses dots around the symbol of the element. The number of dots equals the number of valence electrons in the atom.
- Count the number of valence e- each atom brings into the molecule.For ions, the charge must be taken into account.
How many valence electrons in BeCl2?
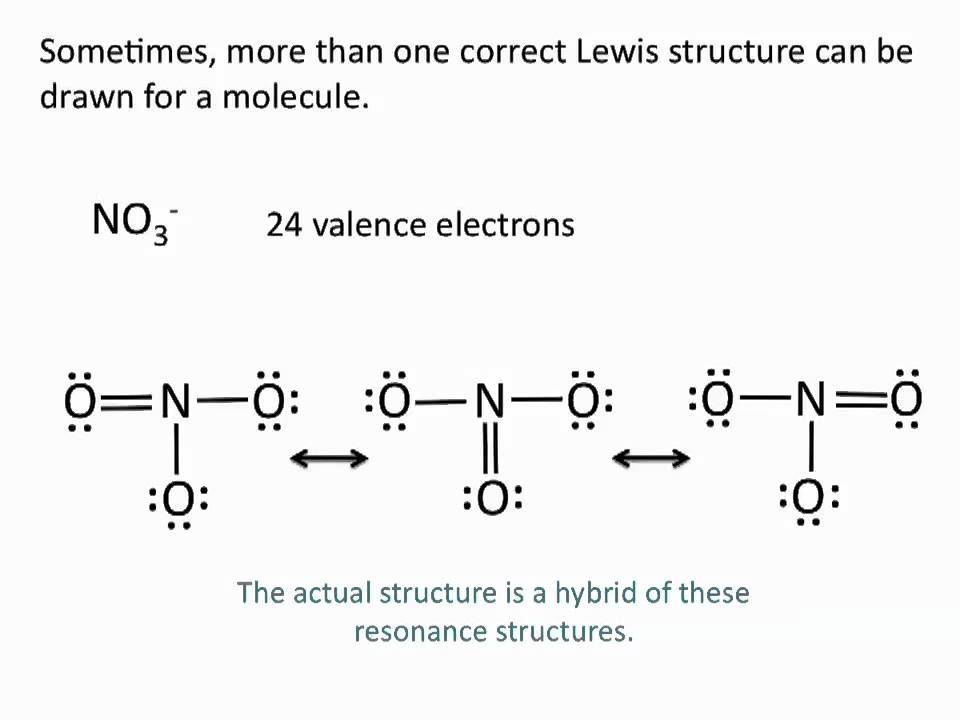
How many valence electrons in NO2- and NO2+?
- Put electron pairs about each atom such that there are 8 electrons around each atom (octet rule), with the exception of H, which is only surrounded by 2 electrons. Sometimes it's necessary to form double and triple bonds. Only C, N, O, P and S (rarely Cl) will form multiple bonds.
Draw the Lewis dot structure for CF4.
The number of valence electrons is 4 + 4 ( 7 ) = 32 electrons.
So, we obtain:
Draw the Lewis dot structure for CO.
The number of valence electrons is 4 + 6 = 10 electrons or 5 pairs. Since both C and O allow multiple bonds we can still follow the octet and write:
- If there is not enough electrons to follow the octet rule, then the least electronegative atom is left short of electrons.
Draw the Lewis dot structure for BeF2.
In BeF2 number of valence e- = 2+ 2(7) = 16 e- or 8 pairs. Since neither Be or F form multiple bonds readily and Be is least electronegative we obtain:
- If there are too many electrons to follow the octet rule, then the extra electrons are placed on the central atom.
Draw the Lewis dot structure for SF4.
In SF4 the number of valence electrons is 6 + 4 ( 7 ) = 34 electrons or 17 pairs. Placing the extra electrons on S we obtain:
How can the octet rule be violated in this last example? The octet rule arises because the s and p orbitals can take on up to 8 electrons. However, once we reach the third row of elements in the periodic table we also have d-orbitals, and these orbitals help take the extra electrons. Note that you still need to know how the atoms are connected in a polyatomic molecule before using the Lewis-Dot structure rules.
Homework from Chemisty, The Central Science, 10th Ed.
8.45, 8.47, 8.49, 8.51, 8.53, 8.55, 8.57, 8.59, 8.61, 8.63
The formation of many common compounds can be visualized with the use of Lewis symbols and Lewis diagrams. In a Lewis symbol, the inner closed shells of electrons can be considered as included in chemical symbol for the element, and the outer shell or valence electrons are represented by dots. The dots are placed in four groups of one or two electrons each, with 8 electrons representing a closed shell or noble gas configuration. Lewis diagrams are useful for visualizing both ionic and covalent bonds.
Lewis Dot Structure Calculator
In the idealized ionic bond, one atom gives up an electron to the other, forming positive and negative ions.
The conditions for bonds are that the total charge is zero and that each atom must have a noble gas electron configuration. |
In the idealized covalent bond, two atoms share a pair of electrons, closing the shell for each of them.
The atoms share a pair of electrons, and that pair is referred to as a bonding pair. The pairs of electrons which do not participate in the bond have traditionally been called 'lone pairs'. A single bond can be represented by the two dots of the bonding pair, or by a single line which represents that pair. The single line representation for a bond is commonly used in drawing Lewis structures for molecules. |